Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) are now confirmed as being multifactorial. In other words, they occur in people genetically predisposed to the disorders after exposure to one or more (as yet unknown) environmental factors.
Causes of autism
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) are now confirmed as being multifactorial. In other words, they occur in people genetically predisposed to the disorders after exposure to one or more environmental factors.
Potential environmental factors include taking certain drugs during pregnancy, being born premature or a lack of oxygen at birth. However, there is solid scientific evidence to rule out the role of vaccines in autism onset.
Epidemiological studies have found a ratio of 3 boys to every 1 girl.
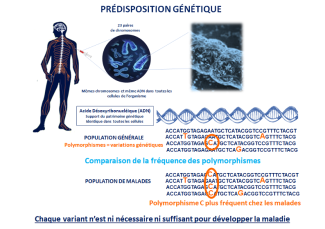
The genetic component is now confirmed by the strong autism correlation in identical twins. We also know that the risk of having a child with ASD is 50 to 100 times higher in the siblings of a person with autism.
Genetics in autism
We have now identified several hundred genes that predispose a person to ASD. These are genetic variants that increase the risk of developing the disease in individuals who carry them. These variants are neither necessary nor enough on their own to develop ASD – a person carrying a given variant does not necessarily have ASD, and a person with autism may not carry this variant.
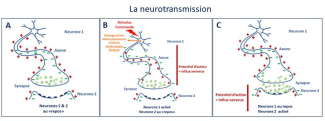
The predisposing genes that have been identified are involved mainly in neurotransmission (passing information from one neuron to another), in synapse formation (the neurotransmission sites) and more generally in brain development.
Clinician-researchers at Paris Brain Institute and the Adult Neurodevelopment Center (CNA), an adult psychiatry department at Pitié Salpêtrière hospital, are setting up a study on the neuroanatomical and functional markers of autism spectrum in adult women. The aim of the study is to compare the MRI data of young women showing signs of autism, but who have no ASD diagnosis, with those of women who do have autism and those of women with no autistic traits.
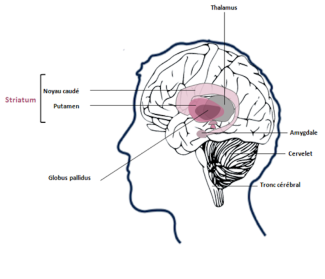
Certain brain anomalies have been identified in people with autism and are located in the ventricles (dilatation), in the cerebellar vermis, in the nuclei of the brain stem or in the hippocampus.
The CHD8 gene is one of the genes that predisposes someone to autism, creating a greater risk of developing the disease. In 2018, Carlos Parras, Inserm researcher on team led by Bassem HASSAN, highlighted the role of the protein encoded by this gene in the differentiation of oligodendrocytes. These central nervous system cells have two essential roles:
- Myelination, i.e. the formation of an insulating and protective sheath for neurons, myelin, to aid the transmission of the nerve message.
- The supply of energy to the neurons, for optimal functioning of these cells
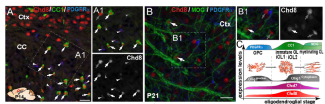
The results of this work show how oligodendrocytes play an important role in the brain anomalies linked to autism spectrum disorders.
At Paris Brain Institute
Clinician-researchers at Paris Brain Institute and the Adult Neurodevelopment Center (CNA), an adult psychiatry department at Pitié Salpêtrière hospital, are setting up a study on the neuroanatomical and functional markers of autism spectrum in adult women.
The aim of the study is to compare the MRI data of young women showing signs of autism, but who have no ASD diagnosis, with those of women who do have autism and those of women with no autistic traits.