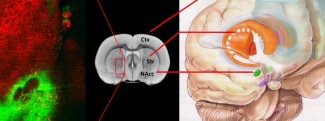
Schizophrenia is a psychiatric condition classed as a chronic mental illness. It is an extremely debilitating but relatively common condition. In France, around 600,000 people suffer from schizophrenia, and a total of 0.7% people worldwide: in other words, around 23 million people.
It generally begins in adolescence or young adulthood, with an age of onset of first symptoms between 15 to 25.
-
1 % de la population mondiale est touchée
-

600 mille personnes touchées en France 23 millions à travers le monde
-

15 / 25 ans âge de déclenchement des premiers symptômes
Elle débute généralement chez l’adolescent ou le jeune adulte avec un âge de déclenchement des premiers symptômes autour entre 15 et 25 ans.
Symptoms of schizophrenia
The disease’s clinical picture varies widely from one individual to the next, with a wide range of possible symptoms. These symptoms can be classed into three groups: positive, negative and cognitive.
- ‘Positive’ symptoms include delusions, feelings of persecution or a range of sensory hallucinations that can affect all the senses (hearing, smell, vision, etc.) ;
- ‘Negative’ symptoms, specifically a decline in normal behavioural functions, including emotional blunting or numbness and apathy;
- Finally, ‘cognitive’ or ‘dissociative’ symptoms, typically generally disorganised thought, combined with impaired memory, concentration or reasoning.
All of these symptoms, and the impairments they generate, are a huge daily
burden for patients in their social, professional and personal lives. The risk of early death is two or even three times higher in individuals with schizophrenia compared to the general population. The suicide rate is also very high, with at least one in two patients making an attempt on their lives.
Diagnosing schizophrenia
It is difficult to diagnose schizophrenia and it often takes a long time. It is often suggested after an initial psychotic or delusional episode. There are now three criteria which, combined, indicate schizophrenia. A distortion of reality, typically with delusional thoughts and hallucinations, emotional impairment and, finally, disorganised thinking. It also very challenging to exclude other conditions with which schizophrenia shares a number of symptoms, such as bipolar disorder or certain neurological conditions when diagnosing and treating this disorder. The variety of symptoms and their similarity with other psychiatric conditions, as well as their fluctuation over time, makes diagnosis difficult, often with long referral periods before receiving a schizophrenia diagnosis.
Treatments for schizophrenia
There are treatments available to help patients, but the high number of varying symptoms makes treatment difficult. Schizophrenia is mainly treated with neuroleptics, drugs that help to control its positive and negative symptoms, but which are not effective against ‘cognitive’ deficits. Up to one third of patients do not respond to these therapies. New therapeutic targets are therefore being actively researched to improve the treatment of schizophrenia, particularly for cognitive deficits. Cognitive-behavioural therapies are, for example, very useful for working with the patient to help with their cognitive deficits and risks of social isolation, and to help bring stability to their daily lives.
A clinical trial under way at Paris Brain Institute is researching the treatment of auditory hallucinations resistant to drug treatment through repeated transcranial magnetic stimulation and to identify the brain mechanisms involved in the effects of this treatment using MRI.
Causes and mechanisms of schizophrenia
Many questions remain unanswered when it comes to the origin and pathophysiology of this disorder. While important information about the role of genetics and the environment has been uncovered, clear mechanisms for the disease’s development have yet to be identified.
Genetic risk factors that increase susceptibility to developing the disease have been identified, as have specific mutations with probable effects on brain plasticity, connection processes in the brain and their adaptation to life experiences and learning.
Understanding these mechanisms is therefore essential in this disease. Several teams at Paris Brain Institute are working to understand neuronal plasticity and sensory perception mechanisms in molecules, cells and networks.
Anatomical changes have been observed in this condition, with damage to the brain’s grey and white matters as well as to its supporting cells such as oligodendrocytes, and to the myelin sheath, which is important in the transmission of nerve impulses. Similarly, the impact of all these factors on brain function continues to be studied.
Environmental factors have also been posited, such as certain types of stress thought to disrupt biological mechanisms in the brain, and the use of psychogenic substances such as cannabis (THC), particularly in adolescents.
Finally, the identification of markers of schizophrenia development and progression, which would be a major step forward in patient care, is a major hope for research.
Support Paris Brain Institute
Did you like this content and did it answer the questions you were asking? Don't hesitate to support Paris Brain Institute.