The signs of a stroke can vary widely: a motor deficit, the face has dropped on one side, an arm that won’t lift normally, difficulties speaking, vision problems or numbness of a limb. They are often lateralised, which means that they only appear on one side of the body.
Diagnosing a stroke
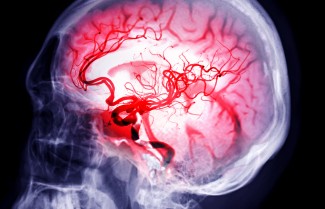
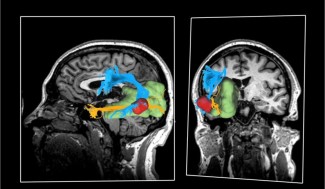
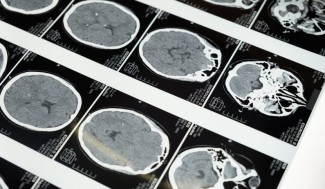
In a hospital setting, brain imaging is also used for stroke diagnosis to confirm and pinpoint the type of stroke (ischemic or haemorrhage).
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the most suitable imaging technique for stroke cases. When a stroke happens, it very quickly locates the area of obstruction in the artery and the extent of the ‘penumbra area’, in order to establish the quickest and most effective treatment.
An ischemic stroke in the right hemisphere of the brain leads to paralysis on the left side of the body (left hemiplegia), problems with vision, dizziness, and loss of coordination. Patients present with a condition called ‘hemi-neglect’. This is because patients lose awareness of the left side of their body and behave as if it did not exist. If the ischemic stroke occurs in the left hemisphere of the brain, patients then present with right hemiplegia and language problems.