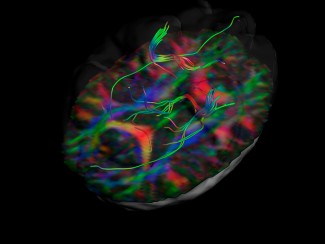
The World Stroke Day for cerebral vascular accidents (CVA) took place on October 29, 2015. The research led at the Institut du Cerveau - ICM seeks to better understand these neurological accidents and to improve the recovery and rehabilitation of patients.
A cerebral vascular accident (CVA) takes place every four minutes in France, which corresponds to more than 130,000 cases each year. During a CVA, a region of the brain is deprived of oxygen and the corresponding tissue dies, leading to consequences that can be more or less severe: motor deficiencies, loss of sensitivity and language problems, and consequences that can led to permanent disability. Care of patients after a CVA and the improvement of their recovery is thus a current need for patients and a major challenge for the Institut du Cerveau - ICM.
Institut du Cerveau - ICM teams seek to understand the mechanisms of cerebral plasticity that occurs after a CVA, to aid in recovery of patients thanks to transcranial magnetic stimulation, developing therapeutic games to rehabilitate patients, and develop diagnostic tools to predict outcomes for patients who are victims of brain lesions.
COMPENSATE FUNCTION LOST BY LESIONS
After a CVA, in certain cases, recovery is possible because the brain is plastic. The team of Paolo Bartolomeo showed that the left hemisphere can compensate for a lesion of the right hemisphere by studying patients suffering from "unilateral spatial neglect." These patients, following a cerebral vascular accident occurring in the right hemisphere of the brain, act as if the left part of the world no longer exists: they do not eat what is on the left side of their plate, knock into furniture situated to their left, do not shave or apply makeup on the left side of their face.
Some patients recover with time, but spontaneous improvement of the neglect is far from being the rule: at least a third of patients continue to suffer from this problem more than a year after their lesion. By following the evolution of 45 patients with this pathology by "diffusion" MRI, the team of Paolo Bartolomeo showed that this neglect persists when it is accompanied by damage of white matter fibers that allow communication between the two hemispheres. If the fibers are not harmed, the two hemispheres can compensate for each other, at least in part, thanks to "cerebral plasticity" mechanisms, which are poorly understood.
The identification of predictive factors for the persistance of neglect is a major clinical challenge because it allows development of a rehabilitation program adapted to patients in which this problem risks becoming chronic.
TREAT WITH TRANSCRANIAL MAGNETIC STIMULATION
Thanks to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Charlotte Rosso in the team of Marie Vidailhet and Stéphane Lehéricy, studies the changes that take place in the brain in order to compensate for the loss of the function in a lesioned region following a CVA.
Three processes can take place:
- Neighboring tissues take control of the functions lost.
- Secondary zones implicated in programming movement can take command of motor control.
- The healthy hemisphere, unaffected by the CVA, can take control of the corresponding zones (as in unilateral spatial neglect)
In order to help the recovery of patients who are victims of CVA, transcranial magnetic stimulation can be used to reinforce the regions of the brain identified by MRI. This technique, used as a diagnostic tool is being tested at the Institut du Cerveau - ICM for treatment.
This technique involves non-invasive brain stimulation that uses a coil placed near the head of an individual to try to make a region more excitable so that it can contribute to compensating for lost function.
This new innovative techniques could allow for development of adapted treatments for every patient.
DEVELOP THERAPEUTIC GAMES
It is critical to care for patients after a CVA in order to improve their recovery and to decrease negative consequences. However, rehabilitation is often repetitive, reaching the therapist can be difficult, and patients become demotivated.
"Voracy Fish" is a therapeutic game or "serious game" that seeks to make rehabilitation fun and find a solution to patients' demotivation. This game, created by the LabCom BRAIN e-NOVATION, a laboratory affiliated with the Institut du Cerveau - ICM and the GENIOUS group, coordinated by Marie-Laure Welter and Pierre Foulon, aims to functionally rehabilitate the upper limbs of patients who have suffered from a CVA.
Patients can play on their own, with their families, or in a network with other patients, at home or in a healthcare facility. The establishment of a technical platform allows for therapists to record different parameters of patients' motor behavior in order to suggest an adjustment of the video game in function of the progress and needs of the patient.
This type of innovative treatment takes into account the different components of behavior: motor function with movements of the body, cognition with the stakes and objectives for different levels of the game, and finally, the emotional and motivation aspects thanks to the fun side of the device. Brain e-novation records these games in clinical research protocols in order to show interest and the efficiency of this type of treatment.
PREDICTING PATIENT OUTCOME
Lesions resulting from a CVA or from a traumatic brain injury could lead to consciousness troubles followed by a coma if the prognosis is uncertain.
After taking patients into the intensive care unit to help their survival, patients can awaken quickly and regain consciousness or remain in a vegetative or minimally-conscious state (defined by eye opening with partial consciousness possible but insufficient for essential communication).
In this case, the clinicians ask what is the possibility of reversibility of the lesions provoked by the stroke. Can consciousness be restored in a temporary or permanent fashion? Will the patients wake up? If the answer is yes, will they recover completely, partially, or will they be left handicapped? And with what delay?
In order to answer these questions, Prof. Louis Puybasset developed a tool to predict patient outcome with a multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan because clinical exams are insufficient.
Multimodal MRI is a system to analyze the brain that allows quantification of patients' lesions, identification of the structures that have been lesioned, and evaluation of the integrity of the connections between the different regions of the brain. This is particularly important because certain regions are more critical than others for awakening.
A computer system for analysis of MRI data combined with a mathematical model allows a high reliability prediction of whether patients will wake up or remain in a vegetative or minimally-conscious state within a year.
The creation of international data banks of the multimodal MRI patient data is established. This allowed creation of a vast operational expert network "comaweb" so that reliable expert reports can be provided from the first weeks of coma, in terms of neurological prognosis, to help clinicians from around the world in their decision making.
Trois processus peuvent se mettre en place :
- une prise en charge de la fonction perdue par les tissus environnants
- une participation à la commande d’un mouvement par les aires secondaires impliquées dans la programmation d’un mouvement
- une prise en charge par les aires correspondantes de l’hémisphère sain, non touché par l’AVC (comme dans la négligence spatiale unilatérale)
Afin d’aider la récupération des patients victimes d’AVC, la Stimulation Magnétique Trans-Crânienne (SMTC) peut être utilisée pour renforcer les zones du cerveau identifiées par IRM. Cette technique, utilisée pour le diagnostic est testée à l’Institut du Cerveau – ICM en terme de traitement.
Il s’agit d’une stimulation cérébrale non invasive à l’aide d’une bobine posée en regard du crâne de l’individu, qui va essayer de rendre une région plus excitable pour qu’elle contribue à compenser la fonction perdue.
Ces nouvelles techniques innovantes permettraient de développer un traitement adapté à chaque patient.
Développer des jeux thérapeutiques
Prendre en charge les patients après un AVC pour améliorer leur récupération et atténuer les séquelles est indispensable. Cependant la rééducation est souvent répétitive, il est parfois difficile d’accéder au thérapeute et les patients peuvent se démotiver.
« Voracy Fish » est un jeu thérapeutique ou “serious game” qui a pour objectif de rendre cette rééducation ludique et de remédier à la démotivation des patients. Ce jeu, créé par le LabCom BRAIN e-NOVATION, laboratoire commun entre l’Institut du Cerveau – ICM et le groupe GENIOUS, coordonné par Marie-Laure Welter et Pierre Foulon, vise à la rééducation fonctionnelle des membres supérieurs des patients ayant souffert d’un AVC.
Les patients peuvent jouer seuls, en famille ou en réseau avec d’autres patients, à domicile ou en milieu institutionnel. La mise en place d’une plateforme technologique permet au thérapeute de recueillir différents paramètres du comportement moteur du patient afin de proposer un ajustement du jeu vidéo en fonction de la progression et des besoins du patient.
Ce type de traitement innovant prend en compte les différentes composantes du comportement : la motricité avec les mouvements du corps, la cognition avec les enjeux et des objectifs de réussite des différents niveaux de jeu, enfin l’aspect émotionnel et motivationnel grâce au côté ludique du dispositif. Brain e-novation inscrit ces jeux vidéo dans des protocoles de recherche clinique pour montrer l’intérêt et l’efficacité de ce type de traitement.
Prévoir le devenir des patients
Les lésions provoquées par un AVC ou par un traumatisme crânien peuvent entraîner un trouble de la conscience suivi d’un coma dont le devenir est incertain.
Après la prise en charge immédiate des patients en réanimation pour permettre leur survie, le malade peut se réveiller rapidement et retrouver sa conscience ou rester dans un état végétatif ou pauci-relationnel (défini par l’ouverture des yeux avec une conscience partielle possible mais insuffisante pour qu’une communication fonctionnelle puisse s’établir).
Dans ce cas, la question que se posent immédiatement les cliniciens est celle de la réversibilité des lésions provoquées par l’accident. La conscience est-elle atteinte de façon définitive ou temporaire ? Les patients vont-ils se réveiller ? Si oui, vont-ils récupérer totalement, partiellement ou avec des séquelles très invalidantes ? Et dans quels délais ?
C’est pour répondre à ces questions, que le Pr Louis Puybasset a mis au point un outil pour prédire le devenir des patients grâce à un examen par Imagerie par Résonance Magnétique (IRM) multimodale, car l’examen clinique ne suffit pas.
L’IRM multimodale est un système d’analyse du cerveau qui permet de quantifier les lésions du patient, d’identifier les structures cérébrales lésées et d’évaluer l’intégrité des connexions entre les différentes régions du cerveau. En effet, certaines régions sont beaucoup plus importantes que d’autres en termes d’éveil.
Un système informatique d’analyse de ces IRM allié à un modèle mathématique permet de pronostiquer avec une grande fiabilité si le patient se réveillera ou s’il restera dans un état végétatif ou pauci-relationnel à un an.
La création de banques internationales à partir des données d’IRM multimodale de patients se met en place. Ceci a permis de créer un vaste système expert opérationnel « comaweb » afin que des rapports d’expertise fiables puissent être fournis dès les toutes premières semaines du coma en termes de pronostic neurologique pour assister les cliniciens du monde entier dans leurs prises de décisions.