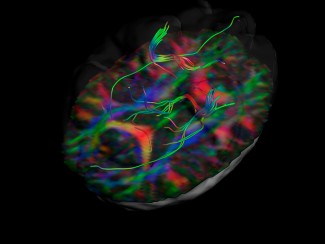
Is paying attention to the things around us necessary to perceive them? This seemingly simple question is far from having a consensual answer. To decide between the various existing hypotheses, Jianghao Liu and his colleagues at Paris Brain Institute studied attention processing in the frontoparietal networks by observing the neural activity of patients fitted with depth electrodes. Using behavioral tests validated by tractography and computer modeling, the researchers show that distinct neural circuits enable attention to be focused and redirected – and that our awareness of the world largely depends on their activity. These results are published in Communications Biology.
Almost half of patients who experienced a stroke in the right cerebral hemisphere later develop a very unusual symptom: they lose the ability to perceive what is happening in the left side of space. As a result, they tend to eat only the right side of their plate, ignore people on their left, and have great difficulty finding their way around. This disorder, known as hemispatial neglect, does not involve basic visual abilities, which remain intact.
“These patients see very well. The problem lies elsewhere! They are not aware of a part of their environment, not because they do not receive visual information, but because they are not paying attention to it, describes Paolo Bartolomeo, neurologist, and researcher at Paris Brain Institute. The treatment of these patients consists, in a way, of re-educating their attention abilities.”
How could we possibly not be aware of elements of reality that we do perceive? To answer this question, we need to understand the nature of the relationship between consciousness and attention. Researchers have been trying to formalize it for many years, but several competing theories coexist, none of which has prevailed. To find out more, Paolo Bartolomeo and Jianghao Liu, a doctoral student in the PICNIC team, decided to put these theories to the test.
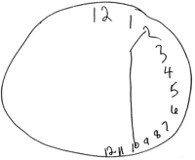
Patients with hemispatial neglect only consider visual stimuli on one side of space, even though there may be no sensory loss. The clock test is traditionally used to assess changes in their abilities during rehabilitation.
Gabor to starboard
We wanted to describe the interactions between attention and conscious perception in the finer details, not only to elucidate attention disturbances in certain cognitive disorders but also to better understand human consciousness in general. Clinical studies tell us that attention is necessary, though not sufficient, for conscious perception, but we didn't know how this is translated in the brain. Thus, we tried to uncover the mechanisms of attention processing in frontoparietal networks.
To shed light on these questions, the researchers focused on so-called exogenous attention, i.e., attention focused on environmental stimuli. Conventional neuroimaging techniques such as fMRI and EEG are insufficient to obtain precise data on brain activity during cognitive tasks. The team, therefore, used intracerebral electrophysiological recordings from 13 epileptic patients who had been implanted with deep brain electrodes to treat drug-resistant epilepsy.
Participants in the study were asked to perform a cognitive task that involved detecting a target called a Gabor patch, which can become barely discernible by changing the contrast of the black and white bars composing it. The target appeared on the left or right of a screen and was preceded by a visual cue (a simple black dot) – either correct (announcing the side on which the target appeared) or misleading (announcing the wrong side). In some cases, the Gabor patch did not appear at all.

Supporting neural evidence
“This experiment allowed us to determine that manipulating the participants' attention via the visual cue could modify their ability to consciously perceive the Gabor patch and describe what they had seen, explains Jianghao Liu. Their attention capacities were either inhibited or increased tenfold depending on the stimuli. At the same time, we observed that specific neural networks were involved in the different types of interaction between attention and conscious perception.”
More specifically, through electrophysiological recording, the researchers identified five clusters of electrical activity associated with the maintenance and redirection of attention in frontoparietal networks. They then used white matter tractography, an imaging technique, to encure that these clusters matched the architecture of anatomically observable neural projections. Finally, they checked the robustness of these results using a computer model to ensure that the neural dynamics they observed were not specific to epileptic patients and could be generalized eventually.
For the first time, we have been able to map the areas of the brain involved in the interaction between attention and conscious perception. This is a great advance: certain current hypotheses claim that conscious perception and attention are two functions perfectly isolated from each other and rely on different networks. Our data shows the opposite.
Ces interactions entre attention et perception consciente façonnent très certainement notre perception du monde, dans la mesure où notre attention est constamment attirée par de nouveaux événements, petits ou grands, dans notre environnement immédiat. « A présent, nous souhaitons déterminer si l’attention aux événements endogènes – c’est-à-dire issus de nos pensées, de nos sensations internes, bref, de notre vie intérieure, pourrait également avoir un effet sur la conscience, conclut Paolo Bartolomeo. Après tout, notre capacité à être attentifs à nous-mêmes est aussi fascinante que notre faculté à percevoir le reste de l’univers. »
Funding
This work was funded by the ANR, the Foundation for Stroke Research, the AP-HP Foundation, and Dassault Systèmes.
Sources
Liu J. et al. Fronto-parietal networks shape human conscious report through attention gain and reorienting. Communications Biology (15 juillet 2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-023-05108-2.