Friedreich’s ataxia (AF) is the most common autosomal recessive genetic cerebellar ataxia and affects about 1300 people in France, with symptoms usually occurring between the ages of 7 and 14.
-

1 300 Personnes concernées En France
-

7-14 Ans Âge d'apparition des premiers symptômes
This ataxia is due to mutations in the FXN gene, which encodes a protein called FRATAXINE that regulates the amount of iron in the mitochondria, a small structure essential for the survival of cells such as neurons.
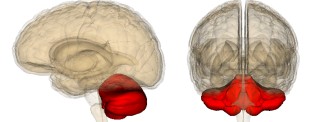
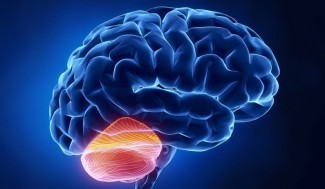
When frataxin is mutated, it accumulates in the mitochondria, leading to dysfunction of the cerebellum. Symptoms of the disease are caused by the disappearance of certain neurons and heart cells.
In 90% of cases, the disease begins with neurological symptoms, walking instability, falls, and coordination problems. More rarely, scoliosis (deformity of the spine), plantar arch deformity or cardiomyopathy (weakness of the heart muscle) are the first clinical signs.
Insulin-dependent diabetes associated with balance disorders in a child or adolescent may suggest Friedreich’s ataxia.
In 96% of cases, the diagnosis was confirmed by molecular analysis, which showed homozygous pathological expansion of GAA triplets (between 70 and 1700 repeats) in the first intron of the FXN gene. In 4% of cases, sequencing of the frataxin gene for a mutation other than expansion is required.
Curative treatment for Friedreich’s ataxia is not yet available. Research is active in the field with many innovative therapeutic avenues: improving mitochondrial function and reducing oxidative stress, modulating the pathways controlled by the frataxin protein, replacing/stabilizing/activating the frataxin protein, increasing the expression of the FXN gene and bringing in a functional FXN gene (gene therapy).
Comprehensive and early management is essential in order to preserve as much as possible the autonomy, the functional capacities, and to prevent and treat certain complications (neurological, osteoarticular, cardiac, and diabetological etc. ).
A multidisciplinary follow-up must be set up in conjunction with a neuropaediatrician/neurologist, a doctor of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, a cardiologist, and other specialists if necessary (diabetologist, ophthalmologist, ENT specialist, orthopaedist), psychologists and paramedical professionals (physiotherapist, speech therapist, social assistant, occupational therapist, etc.).
Centre de Référence Neurogenetique, which contains the map and coordinates of the sites on the territory, as well as current research: http://brain-team.fr/crmr-neurogene/