Deepen our understanding of the human brain during development
The BFGP program aims to tackle the following key questions:
- What are the molecular signatures of human brain cells across age in health and disease?
- What are the functions of key genes in brain development, function and disease?
The project's goals
The main goal of the program is to deepen our understanding of the human brain during development by linking gene expression locations to their functions, by providing to the wide community focusing in neurological and neurodegenerative diseases established, robust techniques and characterized tools.
Aim1: Atlas of the human and mouse brain molecular signature in development
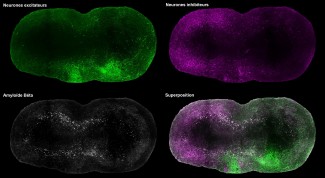
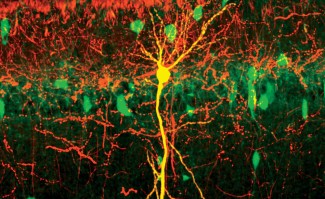
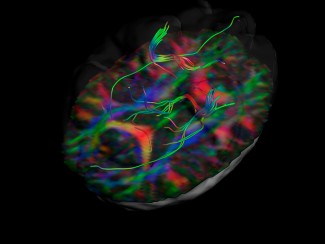
We will leverage our expertise in state-of the art technologies to perform 3D visualization(iDISCO) of transcripts, combined with spatial transcriptomics on the human fetal brain, and mouse brain in development. We will develop strategies for large samples imaging, with the goal not only to develop an atlas of the human brain but also to provide a complete pipeline from protocol to analysis to the community.
Aim2: Functional screening of disease-causing genetic variants in neurogenesis
The goal is to build an IPSC library of characterized clones. We will build a guide-RNA library for the whole genome through gene silencing (CRISPR interference). This library will serve to generate individual IPS cell lines that will be screened in 2D. More complex models, such as organoids, will be used in a later phase of the program.
Aim3: Machine learning assisted quantification of cell types
Establish connections between the datasets (Aims 1 and 2) using ML