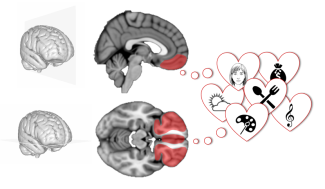
Estimating the value of alternative options is a key process in decision-making. Human functional magnetic resonance imaging and monkey electrophysiology studies have identified brain regions, such as the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) and lateral orbitofrontal cortex (lOFC), composing a value system.
In the present study, in an effort to bridge across species and techniques, we investigated the neural representation of value ratings in 36 people with epilepsy, using intracranial electroencephalography.
We found that subjective value was positively reflected in both vmPFC and lOFC high-frequency activity, plus several other brain regions, including the hippocampus. We then demonstrated that subjective value could be decoded (1) in pre-stimulus activity, (2) for various categories of items, (3) even during a distractive task and (4) as both linear and quadratic signals (encoding both value and confidence). Thus, our findings specify key functional properties of neural value signals (anticipation, generality, automaticity, quadraticity), which might provide insights into human irrational choice behaviors.
Sources
Four core properties of the human brain valuation system demonstrated in intracranial signals, Nature Neurosciences 2020.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-020-0615-9