A study conducted by Julien Boetto and Franck Bielle (Sorbonne University. AP-HP) of the "Genetics and Development of Nervous System Tumours" team at the Paris Brain Institute highlights the potential of GAB1 as a new biomarker for Hedgehog-activated anterior skull base meningiomas. This discovery, published in Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology opens the way to a better diagnosis of these tumours and the development of targeted therapeutic strategies.
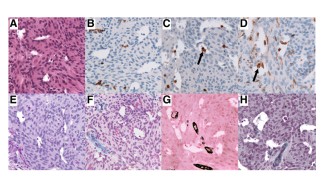
Mutations activating the Hedgehog (Hh) signalling pathway have been described in anterior skull base meningiomas, raising hope for the use of targeted therapies. However, identification of Hh-activated tumours is hampered by the lack of a reliable immunohistochemical marker. Researchers report the evaluation of GAB1, an immunohistochemical marker used to detect Hh pathway activation in medulloblastoma, as a potential marker of Hh-activated meningiomas.
GAB1 staining was compared to SMO mutation detection with Sanger and NGS techniques as well as Hh pathway activation study through mRNA expression level analyses in a discovery set of 110 anterior skull base meningiomas and in a prospective validation set of 21 meningiomas.
Using an expression score ranging from 0 to 400, they show that a cut-off score of 250 lead to excellent detection of Hh pathway mutations (sensitivity 100%, specificity 86%). The prospective validation set confirmed the excellent negative predictive value of GAB1 to exclude Hedgehog independent meningiomas. The team describe a large series of 32 SMO-mutant meningiomas and define multiple ways of Hh activation, either through somatic mutations or associated with mutually co-exclusive SHH (Sonic Hedgehog) or IHH (Indian Hedgehog) overexpression independent of the mutations.
The assessment of GAB1 expression by an immunohistochemical score is a fast and cost-efficient tool to screen anterior skull base meningiomas for activation of the Hedgehog pathway. It could facilitate the identification of selected cases amenable to sequencing for hedgehog pathway genes as predictive markers for targeted therapy.
Sources
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34056767/
Boetto J, Lerond J, Peyre M, Tran S, Marijon P, Kalamarides M, Bielle F. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2021 May 31