Myelin, a protective sheath that covers various nerve fibers, is essential in the transmission of nerve signals and enables proper function of the nervous system. Myelin degeneration causes severe illnesses including multiple sclerosis. Lamia Bouslama-Oueghlani from the team led by Brahim Nait Oumesmar at Paris Brain Institute and collaborators proved that the Pak3 gene, involved in certain types of intellectual disabilities, regulates myelin sheath formation.
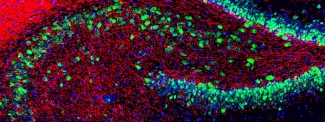
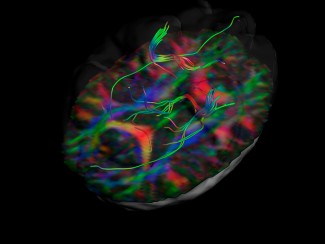
Myelin plays a critical role in nerve signal transfer as well as in axonal protection and support. It is necessary to ensure proper function of the nervous system, and myelin deficit is observed in severe pathologies including multiple sclerosis and leukodystrophy. Oligodendrocytes are the key cells in the development process.
Myelin and oligodendrocyte deficit is also described in several mental/psychiatric illnesses; recent studies highlighted the critical role played by myelin plasticity in cognitive and behavioral functions. Oligodendrocytes could therefore be targeted in neuropsychiatric pathologies including depression, autism and schizophrenia.
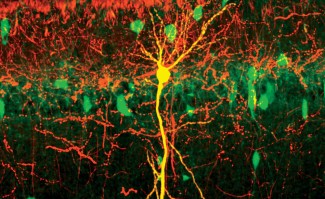
In this context, Pak3 is of particular interest. Several Pak3 genetic mutations were identified in mental illnesses with intellectual disability. PAK3 protein is expressed in the brain, where its action has mainly been studied in neurons but not in glial cells. However, Pak3 is expressed in oligodendrocytes and precursors, cells that are to become oligodendrocytes after differentiation and maturation.
For the first time, a research project involving the team led by Brahim Nait Oumesmar has focused on effects of a loss of function in gene Pak3 on oligodendrocyte and myelination development.
Researchers highlighted strong PAK3 protein expression in oligodendrocyte precursors, notably lowered in mature oligodendrocytes. The team found that loss of Pak3 function leads to poor differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursors and poor myelin sheath development is certain areas of the brain. However, it appears that in adults poor differentiation may be compensated by mature oligodendrocytes in terms of oligodendrocyte density as well as axon myelination.
Researchers also focused on the effects of lack of Pak3 at cellular level by comparing proliferation, migration and differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cultures with or without Pak3 expression. Results show that
PAK3 acts as a regulator of oligodendrocyte precursor differentiation.
The next step is studying how PAK3 acts on oligodendrocyte precursors, and understanding its involvement in mental and psychiatric illnesses.
Sources
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27940202/
Maglorius Renkilaraj MR, Baudouin L, M Wells C, Doulazmi M, Wehrlé R, Cannaya V, Bachelin C, Barnier JV, Jia Z, Nait Oumesmar B, Dusart I, Bouslama-Oueghlani L.