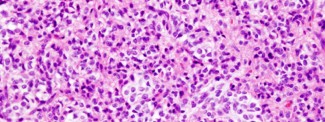
Among the many different types of tumors developing from the brain, diffuse gliomas are the most frequent. Their characteristics make them very difficult to treat and relapses are frequent. Dr Frank Bielle from the Experimental Neuro-oncology team looked at the features of tumor cells in a specific form of diffuse glioma, anaplastic oligodendroglioma. He showed that tumor cells are very heterogeneous and he identified a sub-set of cells which could be of major importance in tumors’ relapse. These results, published in Brain Pathology, open new therapeutic avenues overcoming resistance to current anti-tumor treatments.
Brain tumors are very diverse. One type of tumor, diffuse gliomas, is particularly difficult to treat. These tumors develop in the brain tissue and are often not well defined; Neurosurgeons thus cannot remove them completely and a complementary medical treatment (chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy) is needed most of the time.
Anaplastic oligodendrogliomas belong to the diffuse gliomas family. Tumor cells carry mutations on IDH genes and a chromosomal abnormality (1p/19q chromosomal regions co-deletion). Over these mutations, tumor cells mimic the shape of oligodendrocytes (support cells for the nerves in healthy brain). Anaplastic oligodendrogliomas are more sensible to chemotherapies than other diffuse gliomas; nonetheless they tend to relapse and become resistant to the therapies currently available.
Progress have been made in the classification of diffuse gliomas thanks to the identification of mutations (modifications in the DNA) but the functioning of tumor cells and their morphology remain to be clarified.
Dr Frank Bielle from the Experimental Neuro-oncology team looked at the characteristics of the tumor’s cells in anaplastic oligodendroglioma. This work wouldn’t have been possible without the participation of physicians and patients from all over France gathered under the POLA Network for “rare tumors”, coordinated by Pr J-Y Delattre and Pr D. Figarelle-Branger, without the support of the l’Association pour la Recherche sur les Tumeurs Cérébrales and the Fondation ARC pour la recherche sur le Cancer and without the la Ligue Nationale contre Cancer which funded the molecular analysis of tumors.
Surprisingly, the researchers observed that certain cells in the tumor showed features of intermediate neuronal progenitors, cells at the origin of new neurons. Neuronal progenitors are, in adults, limited to very specific areas of the brain, specialized in the production of new neurons. Yet, in the places where oligodendrogliomas develop, mainly in the frontal lobe of the brain, there are normally no neuronal progenitors in adults.
They also showed a great intertumor (i.e differences between two individuals in the characteristics of their tumor) and intratumor (i.e in the tumor where some cells look like neuronal progenitors and others have a phenotype closer to regular oligodendrocytes) heterogeneity.
Moreover, by comparing in patients, the first tumor observed and the tumor observed in case of relapse despite the treatment, the scientists showed an increase of tumor cells with neuronal progenitors’ features. This suggests that cells with neuronal progenitors’ characteristics are more and more numerous when the tumor becomes resistant to initial treatments.
For the first time, researchers showed the presence of different types of cells among tumors. These results bring out many interrogations regarding the treatment of tumors. Will a treatment affect both types of cells or just one specifically? Could the resistance to treatments originate from the inefficacy of treatments on one of the two types of cells?
A better understanding of this tumor cells’ heterogeneity in anaplastic oligodendrogliomas open new therapeutic avenues to treat tumors and overcome resistance to current anti-tumor treatments.
Sources
Tumor cells with neuronal intermediate progenitor features define a subgroup of 1p/19q co-deleted anaplastic gliomas. Franck Bielle, François Ducray, Karima Mokhtari, Caroline Dehais, Homa Adle-Biassette, Catherine Carpentier, Anaïs Chanut, Marc Polivka, Sylvie Poggioli, Shai Rosenberg, Marine Giry, Yannick Marie, Charles Duyckaerts, Marc Sanson, Dominique Figarella-Branger, Ahmed Idbaih, Pola Network. Brain Pathology, August 2016.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27543943